Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Fuchi, Aoi*; Sato, Atsushi*; Shibata, Takanori*; Kinsho, Michikazu
no journal, ,
The high-intensity proton accelerator adopts a charge exchange injection scheme, which injects with exchanging from negative Hydrogen ion to proton by using carbon foil. This scheme is destructive-type method by using the foil and can accumulate high intensity proton beam. However, the uncontrolled beam losses by scattering at the foil and the foil breaking by the beam collision are a key issue of high-intensity proton accelerator in the world. In the J-PARC, we newly propose a laser stripping injection scheme of nondestructive-type method as an alternative to the foil and are under development for a proof-of-principle experiment of the method. In my presentation, we introduce an overview of laser stripping injection. Additionally, we report the status of the development and the schedule of the experiment.
Fuchi, Aoi*; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*; Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Sato, Atsushi*; Shibata, Takanori*; Kinsho, Michikazu
no journal, ,
In the J-PARC as high-intensity proton accelerator, beam injection into a synchrotron uses for charge exchange process from hydrogen to proton. For higher intensity beam, we study laser development and POP experiment for charge exchange by using laser. In our method, we consider doppler shift and multi process of electron stripping. Therefore, we are developing high power laser and the 5th harmonics. In order to reduce laser power, we must increase the utilization rate of laser. So, we develop multi-pass cavity and beam shaper. In our presentation, we will report about a status of high-repetition laser and optics devices under developing.
Oka, Makoto
no journal, ,
I discuss the roles of diquarks in heavy baryon spectrum. Using a chiral effective theory of diquarks, we analyze the spectrum and structure of diquark and heavy baryons consisting of diquarks. UA(1) anomaly is considered in the chiral Lagrangian and its effects are studied.
 Np isomer
Np isomerAsai, Masato; Suekawa, Yoshihide*; Higashi, Masato*; Kamada, Hiroki*; Tobe, Teruhisa*; Andreyev, A. N.; Hirose, Kentaro; Ito, Yuta; Makii, Hiroyuki; Nishio, Katsuhisa; et al.
no journal, ,
We have carried out experiments to study nuclear structure of the new isomer 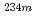 Np which we discovered recently. The
Np which we discovered recently. The 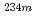 Np was produced in the reaction of
Np was produced in the reaction of  U target with
U target with  Li beam at JAEA tandem accelerator, and was mass-separated with an on-line isotope separator (ISOL). The half-life was determined accurately through LX-ray measurements. The
Li beam at JAEA tandem accelerator, and was mass-separated with an on-line isotope separator (ISOL). The half-life was determined accurately through LX-ray measurements. The  transition emitted by following the isomeric transition was successfully observed through LX-
transition emitted by following the isomeric transition was successfully observed through LX- coincidence measurements. Moreover, the multipolarities of the
coincidence measurements. Moreover, the multipolarities of the  transitions were determined with internal-conversion electron measurements. On the basis of these experimental results, We have clarified excitation energy, spin-parity, and nuclear structure of
transitions were determined with internal-conversion electron measurements. On the basis of these experimental results, We have clarified excitation energy, spin-parity, and nuclear structure of 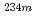 Np.
Np.
 Cf by Coulomb excitation gamma-ray spectroscopy
Cf by Coulomb excitation gamma-ray spectroscopyPham, T. T.; Yanagihara, Rikuto*; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Orlandi, R.; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Makii, Hiroyuki; Hirose, Kentaro; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki
no journal, ,
Utsuno, Yutaka
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sako, Hiroyuki; Sato, Susumu
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sako, Hiroyuki
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
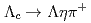 and its sub-decay modes, and observation of
and its sub-decay modes, and observation of 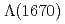
Tanida, Kiyoshi; Belle Collaboration*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Asahi, Yuichi; Fujii, Keisuke*; Dennis, H.*; Maeyama, Shinya*; Idomura, Yasuhiro
no journal, ,
Phase space structures are extracted from the time series of five dimensional distribution function data computed by the flux-driven full-fgyrokinetic code GT5D. Principal component analysis (PCA) is applied to reduce the dimensionality and the size of the data. Phase space bases and the corresponding spatial coefficients (poloidal cross section) are constructed by PCA. It is shown that 83% of the variance of the original five-dimensional distribution can be expressed with 64 principal components, i.e., the compression 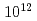 of the degrees of freedom from 10 to
of the degrees of freedom from 10 to 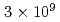 . The relationship between avalanche-like transport phenomena and phase space structure is discussed based on the contribution of each principal component to the heat transport.
. The relationship between avalanche-like transport phenomena and phase space structure is discussed based on the contribution of each principal component to the heat transport.
Yasutake, Nobutoshi*; Mukoubara, Yuta*; Maruyama, Toshiki; Hatsuda, Tetsuo*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Muto, Takumi*; Maruyama, Toshiki; Tatsumi, Toshitaka*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
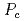 pentaquarks as a hadronic molecule coupling to five-quark states
pentaquarks as a hadronic molecule coupling to five-quark statesYamaguchi, Yasuhiro; Hosaka, Atsushi; Takeuchi, Sachiko*; Takizawa, Makoto*
no journal, ,
We study the 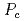 pentaquarks that were reported by LHCb collaboration in 2019. We employ the hadronic molecular model where the one pion exchange potential is introduced as the long-range hadron interaction. As for the short-range interaction, we introduce coupling to the five-quark states in the hadronic molecule. By solving the Schrodinger equation by using the variational method and the complex scaling method, we obtain the energies and decay widths. We also discuss the role of the tensor force and the short-range interaction.
pentaquarks that were reported by LHCb collaboration in 2019. We employ the hadronic molecular model where the one pion exchange potential is introduced as the long-range hadron interaction. As for the short-range interaction, we introduce coupling to the five-quark states in the hadronic molecule. By solving the Schrodinger equation by using the variational method and the complex scaling method, we obtain the energies and decay widths. We also discuss the role of the tensor force and the short-range interaction.
Ishikawa, Tsutomu*; Nakayama, Katsumasa*; Suzuki, Kei
no journal, ,
We propose a definition of the Casimir energy for free lattice fermions. From this definition, we study the Casimir effects for the massless or massive naive fermion, Wilson fermion, and (M bius) domain-wall fermion in
bius) domain-wall fermion in 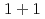 dimensional spacetime with the spatial periodic or antiperiodic boundary condition. For the naive fermion, we find an oscillatory behavior of the Casimir energy, which is caused by the difference between odd and even lattice sizes. For the Wilson fermion, in the small lattice size of
dimensional spacetime with the spatial periodic or antiperiodic boundary condition. For the naive fermion, we find an oscillatory behavior of the Casimir energy, which is caused by the difference between odd and even lattice sizes. For the Wilson fermion, in the small lattice size of 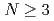 , the Casimir energy agrees very well with that of the continuum theory, which suggests that we can control the discretization artifacts for the Casimir effect measured in lattice simulations. We also investigate the dependence on the parameters tunable in M
, the Casimir energy agrees very well with that of the continuum theory, which suggests that we can control the discretization artifacts for the Casimir effect measured in lattice simulations. We also investigate the dependence on the parameters tunable in M bius domain-wall fermions. Our findings will be observed both in condensed matter systems and in lattice simulations with a small size.
bius domain-wall fermions. Our findings will be observed both in condensed matter systems and in lattice simulations with a small size.